Important Safety Information
Contraindication
- Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim) is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim
- Reactions have included anaphylaxis
Splenic Rupture
- Splenic rupture, including fatal cases, can occur following the administration of Neulasta®
- Evaluate for an enlarged or ruptured spleen in patients who report left upper abdominal or shoulder pain
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- ARDS has occurred in patients receiving Neulasta®
- Evaluate patients who develop a fever and lung infiltrates or respiratory distress after receiving Neulasta®
- Discontinue Neulasta® in patients with ARDS
Serious Allergic Reactions
- Serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis can occur in patients receiving Neulasta®
- Majority of events occurred upon initial exposure and can recur within days after discontinuation of initial anti-allergic treatment
- Permanently discontinue Neulasta® in patients with serious allergic reactions
Allergies to Acrylics
- On-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta® uses acrylic adhesives
- Patients who are allergic to acrylic adhesives may have a significant reaction
Use in Patients With Sickle Cell Disorders
- In patients with sickle cell trait or disease, severe and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur in patients receiving Neulasta®
- Discontinue Neulasta® if sickle cell crisis occurs
Glomerulonephritis
- Has occurred in patients receiving Neulasta®
- Diagnoses based on azotemia, hematuria, proteinuria, and renal biopsy
- Generally events resolved after dose reduction or discontinuation of Neulasta®
- If suspected, evaluate for cause and if cause is likely, consider dose-reduction or interruption of Neulasta®
Leukocytosis
- Increased white blood cell counts of 100 x 109/L have been observed
- Monitoring of complete blood count (CBC) during pegfilgrastim therapy is recommended
Thrombocytopenia
- Thrombocytopenia has been reported in patients receiving pegfilgrastim. Monitor platelet counts
Capillary Leak Syndrome (CLS)
- CLS has been reported after G-CSF administration, including Neulasta®
- Characterized by hypotension, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hemoconcentration
- Episodes vary in frequency, severity, and may be life-threatening if treatment is delayed
- Patients with symptoms should be closely monitored and receive standard symptomatic treatment, which may include intensive care
Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells
- G-CSF receptor has been found on tumor cell lines
- The possibility that pegfilgrastim acts as a growth factor for any tumor type, including myeloid malignancies and myelodysplasia, diseases for which Neulasta® is not approved, cannot be excluded
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) in
Patients With Breast and Lung Cancer
- MDS and AML have been associated with the use of Neulasta® in conjunction with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in patients with breast and lung cancer. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of MDS/AML in these settings
Potential Device Failures
- Missed or partial doses have been reported in patients receiving pegfilgrastim via the on-body injector (OBI) due to the device not performing as intended
- In the event of a missed or partial dose, patients may be at increased risk of events such as neutropenia, febrile neutropenia and/or infection than if the dose had been correctly delivered
- Instruct patients to notify their healthcare professional immediately in order to determine the need for a replacement dose if they suspect that the device may not have performed as intended
Aortitis
- Aortitis has been reported in patients receiving Neulasta®. It may occur as early as the first week after start of therapy
- Manifestations may include generalized signs and symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, malaise, back pain, and increased inflammatory markers (e.g., c-reactive protein and white blood cell count)
- Consider aortitis in patients who develop these signs and symptoms without known etiology. Discontinue Neulasta® if aortitis is suspected
Nuclear Imaging
- Increased hematopoietic activity of the bone marrow in response to growth factor therapy has been associated with transient positive bone imaging changes. This should be considered when interpreting bone imaging results
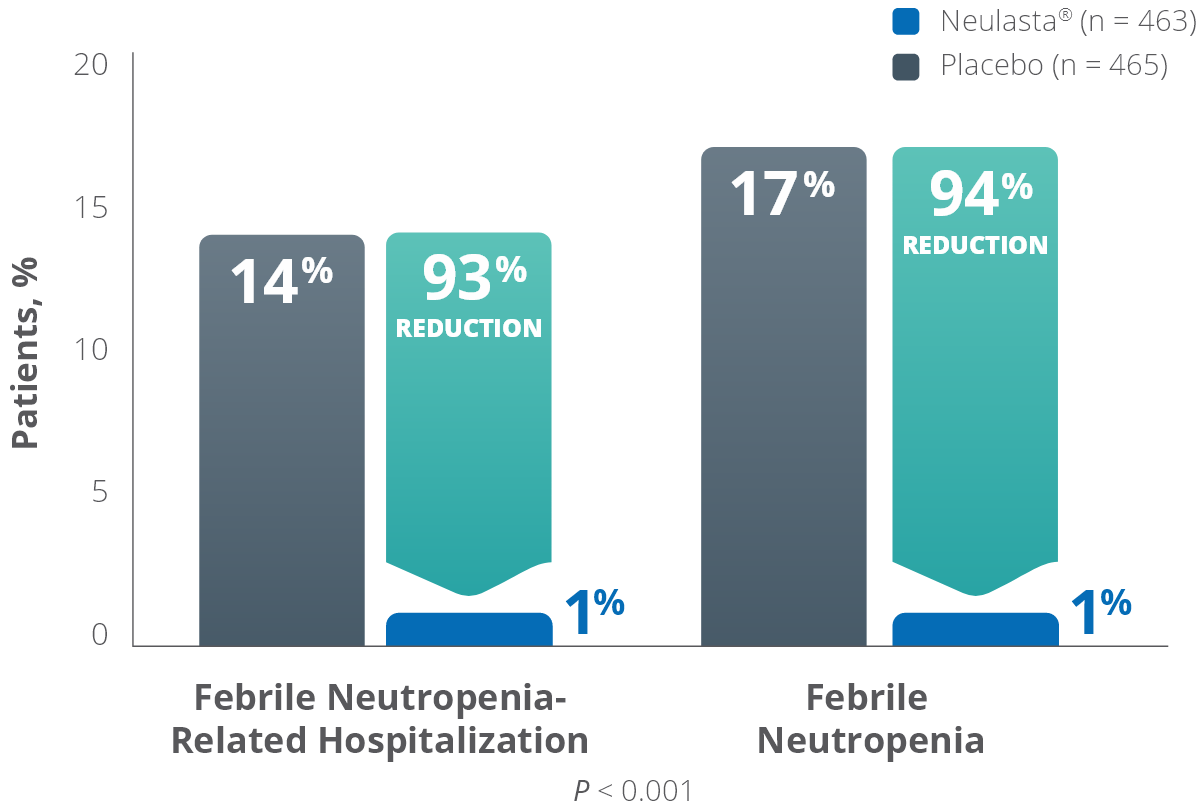
Most common adverse reactions
- Bone pain
- Pain in extremity
Please see Neulasta® full Prescribing Information.
Neulasta® Injection: 6 mg/0.6 mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe for manual use only.
Neulasta® Injection: 6 mg/0.6 mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe co-packaged with the on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta® (Neulasta® Onpro® kit).
Special Instructions for the On-body Injector (OBI) for Neulasta®
A healthcare provider must fill the on-body injector (OBI) with Neulasta® using the co-packaged prefilled syringe and then apply the OBI to the patient’s skin (abdomen or back of arm). The back of the arm may only be used if there is a caregiver available to monitor the status of the OBI. Approximately 27 hours after the OBI is applied to the patient’s skin, Neulasta® will be delivered over approximately 45 minutes. A healthcare provider may initiate administration with the OBI on the same day as the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy, as long as the OBI delivers Neulasta® no less than 24 hours after the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy.
The prefilled syringe co-packaged in the Neulasta® Onpro® kit contains additional solution to compensate for liquid loss during delivery through the OBI. If this syringe is used for manual subcutaneous injection, the patient will receive an overdose. If the prefilled syringe for manual use is used with the OBI, the patient may receive less than the recommended dose.
Do not use the OBI to deliver any other drug product except the Neulasta® prefilled syringe
co-packaged with the OBI. Use of the OBI has not been studied in pediatric patients.
The OBI should be applied to intact, non-irritated skin on the arm or abdomen.
A missed dose could occur due to an OBI failure or leakage. Instruct patients using the OBI to notify their healthcare professional immediately in order to determine the need for a replacement dose of pegfilgrastim if they suspect that the device may not have performed as intended. If the patient misses a dose, a new dose should be administered by single prefilled syringe for manual use as soon as possible after detection.
Review the Patient Information and Patient Instructions for Use with the patient and provide the instructions to the patient.
Refer to the Healthcare Provider Instructions for Use for the OBI for full administration information.
For any OBI problems, call Amgen at 1-800-772-6436 1-800-772-6436 or
1-844-MYNEULASTA
(1-844-696-3852).
1-844-MYNEULASTA
(1-844-696-3852).